Water Surface Profile Computation¶
Background¶
Words here
Two types of methods
Explicit or direct step method: distance is determined for a specified depth change
Mostly for prismatic channels where cross-sectional properties don’t change with distance x.
Implicit methods: depth is computed from distance changes
Unknown appears on both sides of the equation dy = f(y)dx
For natural channels for which cross-sectional properties are determined beforehand at particular locations.
Important Assumptions Slope of the energy grade line, \(S_f\), can be evaluated from Manning’s or Chezy’s equation using the local value of depth.
In either method class, there is a slope averaging component to approximate the energy slope at a section especially impotent in natural channels described in our textbook on pg 185

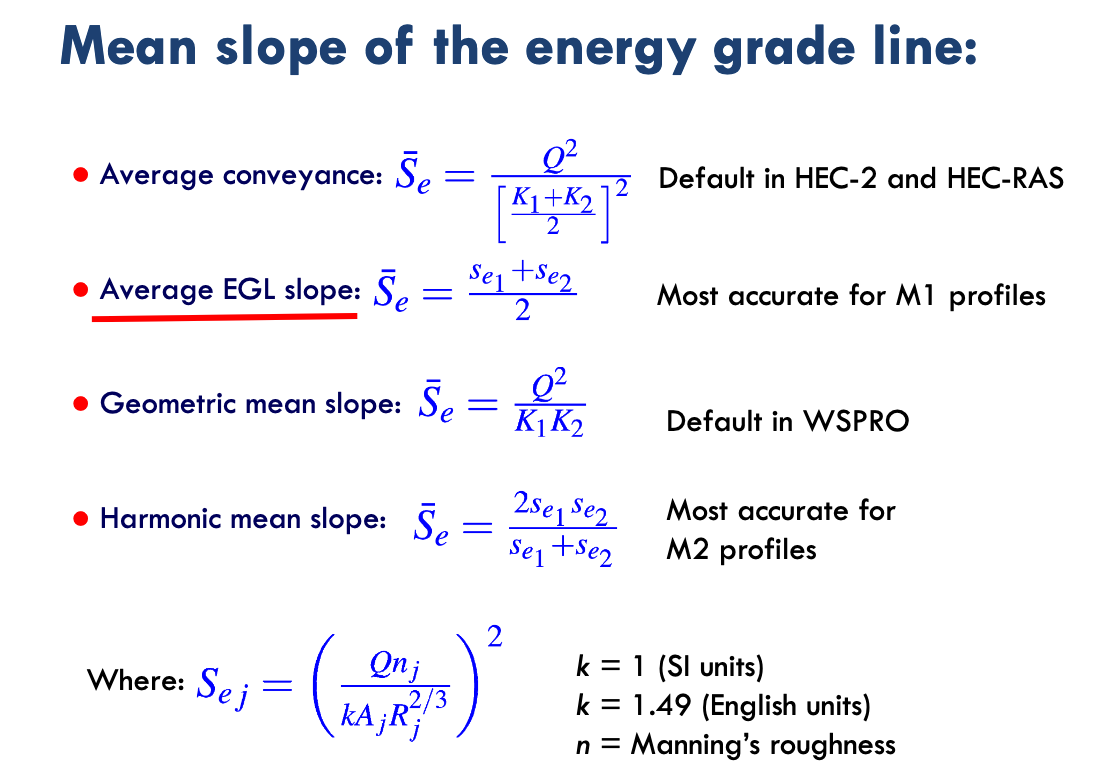
In the scripts in this JupyterBook, the average conveyence is used in the direct step and fixed space step method examples.
Note
In the examples the goal is to illustrate the computational methods employed, averaging the conveyence is just a bit easier programming (not by much). Readers can obviously reverse engineer the scripts and satisfy their own needs.
References¶
Sturm T.W (2001) Open Channel Hydraulics, 1ed., McGraw-Hill, New York. Note: This PDF is from an international edition published in Singapore. http://54.243.252.9/ce-4353-webroot/3-Readings/open-channel-hydraulics-by-terry-w-sturm-www-civilenggforall-com.pdf
