Conservation of Energy (pp. 212-243)¶
Course Website
Energy is a measure of the ability to do work.
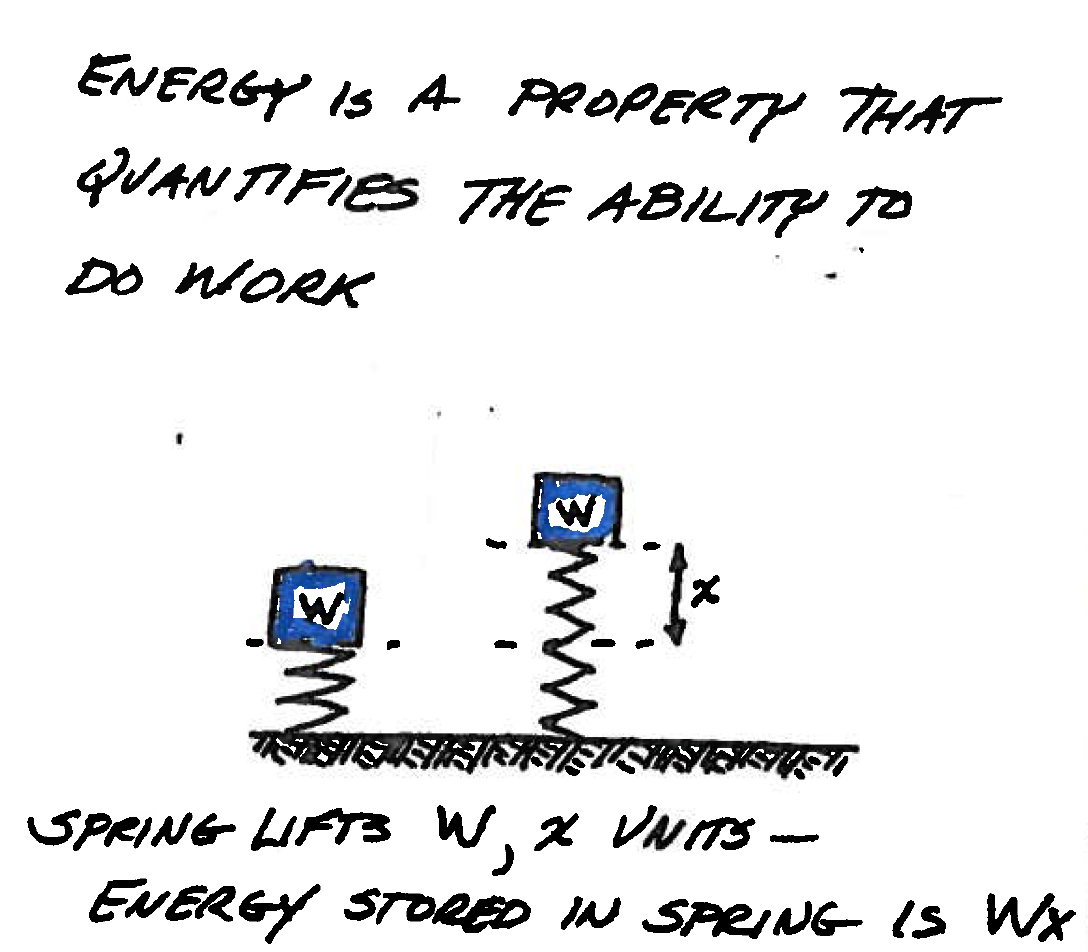
Fig. 100 Caption¶
Some examples include:
water stored behind a dam
wind blowing across a propeller
gasoline burned in a cylinder to push against a piston
Readings¶
CE-3305-2022-1 Syllabus. http://54.243.252.9/ce-3305-webroot/0-Syllabus/ce-3305-2022-1-syllabus.html
Hibbeler, R.C, Fluid Mechanics, 2ed. Prentice Hall, 2018. ISBN: 9780134655413 pp. 293-355
DF Elger, BC Williams, Crowe, CT and JA Roberson, Engineering Fluid Mechanics 10th edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2013. (placeholder file to get links working). http://54.243.252.9/ce-3305-webroot/3-Readings/EFM-10.pdf
Cleveland, T. G. (2014) Fluid Mechanics Notes to Accompany CE 3305 at Jade-Holshule (TTU Study Abroad 2015-2019), Department of Civil, Environmental, and Construction Engineering, Whitacre College of Engineering. http://54.243.252.9/ce-3305-webroot/3-Readings/ce3305-lecture10.pdf
Videos¶
Lesson Outline¶
Definition of energy
Example application
Energy¶
Energy is classified as:
mechanical energy associated with potion or position in a force field
thermal energy is associated with \(\Delta T\) and/or phasse change
chemical energy is associated with breaking chemical bonds to release energy (or creating bonds to absorb energy)
electrical energy is associated with electrical charge in an electric field
nuclear energy is associated with radioactive decay
Units of energy are force*distance:
Joule, \(J = N \cdot m\)
Foot-pound, \( 1 Lb \cdot foot\)
Power is energy per unit time
Watt, \(W = \frac{J}{s}\)
Horsepower \(hp = 550 \frac{ft \cdot lbf}{s}\)
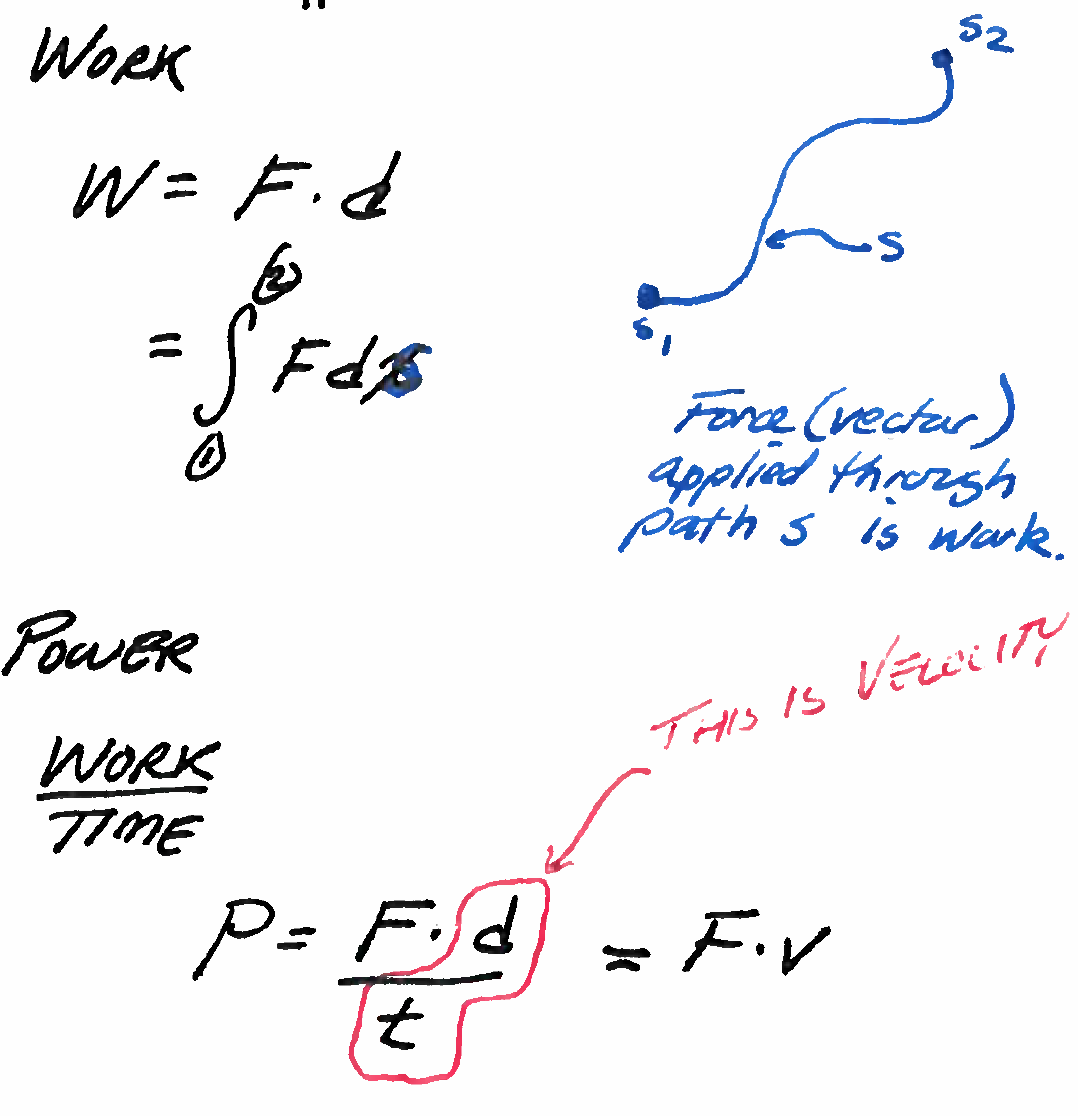
Fig. 101 Caption¶
Example 1:¶
# computational thinning
import math
q = 0.1 #discharge
v_jet = 50.0
omega = 500*2*math.pi/60
radius = 0.5
rho = 1000.0
power = rho*q*v_jet*radius*omega - rho*q*omega**2*radius**2
print("Power ",round(power,2)," Newton-meters/sec ")
Power 62360.77 Newton-meters/sec
