Conservation of Angular Momentum¶
Lesson Outline¶
Definition of angular momentum
Example appliocation
Background¶
Angular momentum (moment of momentum) relates forces to changes in rotational velocity. Reynolds Transport Theorem is used to generate integral expressions of angular momentum balances in a control volume.
The ideas are fundamental in pumps, compressors, turbines, and similar machines.
Angular Momentum¶

Caption¶
angular-p1-1 relates the extensive property of angular momentum for a system to the intensive property of moment of momentum per unit mass which is \(\bar r \times \bar V\).

Caption¶
The result of application of the Reynolds Transport Theorem to the linear momentum term is an integral equation that relates the sum of external forces to the rate of change of linear momentum in the control volume plus the net momentum leaving across the control surface as depicted in angular-p1-2
Example 1: Application of Angular Momentum to a Reaction Turbine¶
Application of angular momentum often involves use of continunity and energy (bernoulli’s equation). Selection of CV is important to make analysis straightforward. Consider the following example involving a reaction turbine (like a Rain-Bird)

The problem statement is depicted in angular-ex1-1
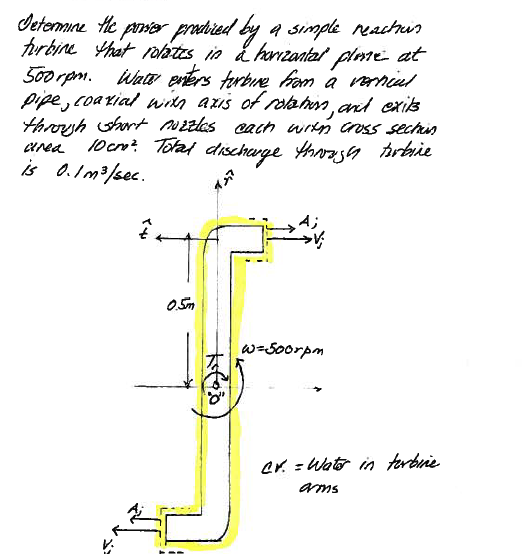
Caption¶
Apply continunity as in angular-ex1-2
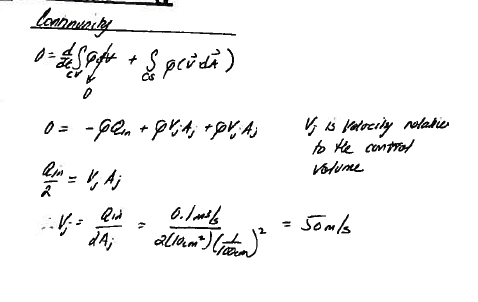
Caption¶
Then momentum as in angular-ex1-3
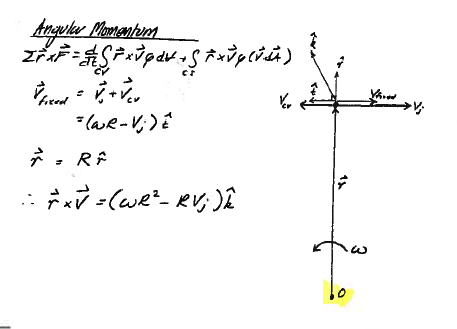
Caption¶
Continue the analysis (break the CV into upper and lower arm, use symmetry to cancel the volume integrals) as in angular-ex1-4

Caption¶
Complete the analysis as in angular-ex1-5
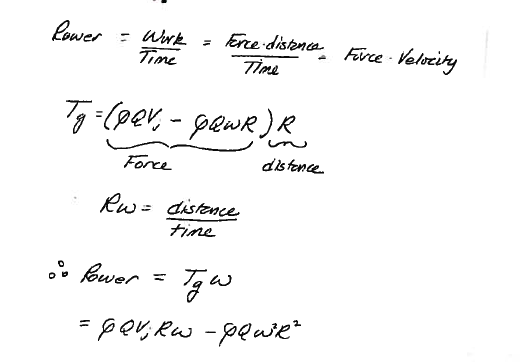
Caption¶
now apply ENGR-1330 to perform the calculations.
# computational thinning
import math
q = 0.1 #discharge
v_jet = 50.0
omega = 500*2*math.pi/60
radius = 0.5
rho = 1000.0
power = rho*q*v_jet*radius*omega - rho*q*omega**2*radius**2
print("Power ",round(power,2)," Newton-meters/sec ")
Power 62360.77 Newton-meters/sec
Example 2: Application of Angular Momentum to a Reaction Turbine¶
Here we will do the same problem, but using a fixed reference frame CV
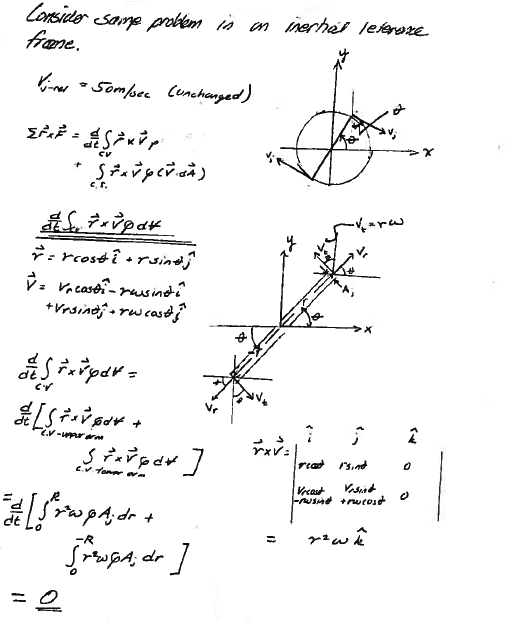
Caption¶
angular-ex1-5 is analysis of the volume integral in a vector representation of the moment of momentum
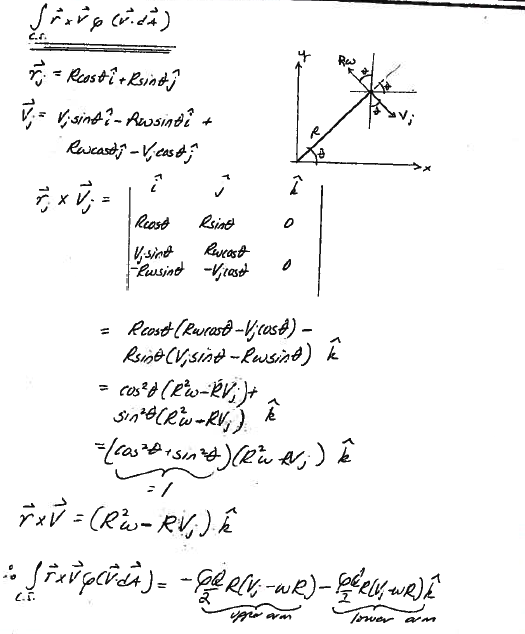
Caption¶
angular-ex1-5 is analysis of the flux integrals in a vector representation of the moment of momentum
After the equations are constructed, the analysys proceedes the same as in the earlier example.
Readings¶
CE-3305-2022-1 Syllabus. http://54.243.252.9/ce-3305-webroot/0-Syllabus/ce-3305-2022-1-syllabus.html
Hibbeler, R.C, Fluid Mechanics, 2ed. Prentice Hall, 2018. ISBN: 9780134655413 pp. 293-355
DF Elger, BC Williams, Crowe, CT and JA Roberson, Engineering Fluid Mechanics 10th edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2013. (placeholder file to get links working). http://54.243.252.9/ce-3305-webroot/3-Readings/EFM-9.pdf
Cleveland, T. G. (2014) Fluid Mechanics Notes to Accompany CE 3305 at Jade-Holshule (TTU Study Abroad 2015-2019), Department of Civil, Environmental, and Construction Engineering, Whitacre College of Engineering. http://54.243.252.9/ce-3305-webroot/3-Readings/ce3305-lecture-9.pdf
