Delineation (by Hand)¶
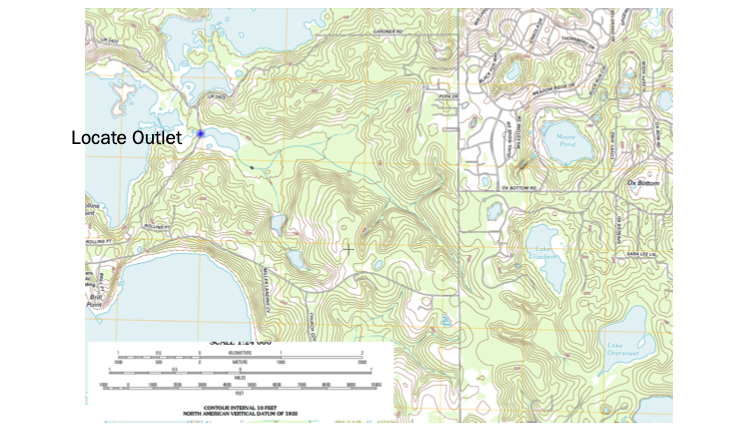
Readings¶
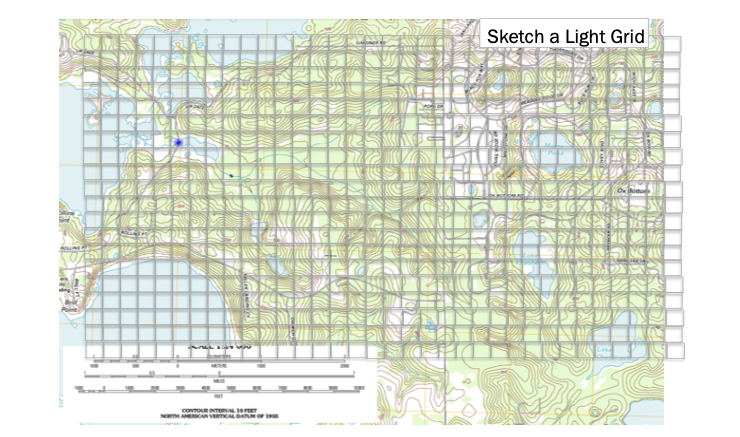
Step 2. Superimpose a Grid¶
While not strictly necessary its helpful. The grid serves two purposes, first a reference system and as a raster representation of the watershed (albeit at a coarse resolution)
Step 3. Cell Elevations¶
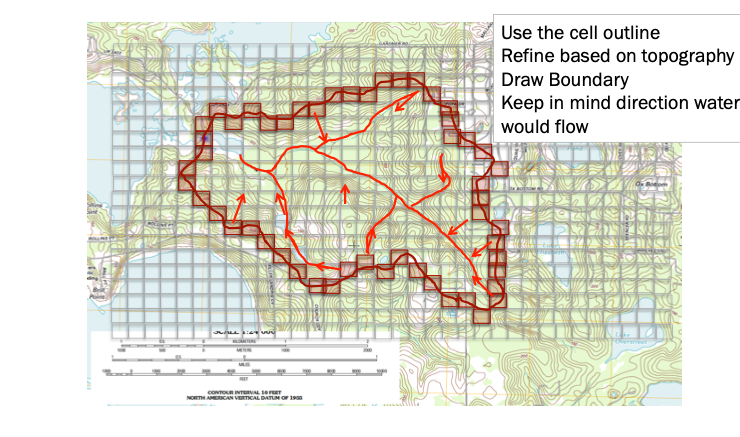
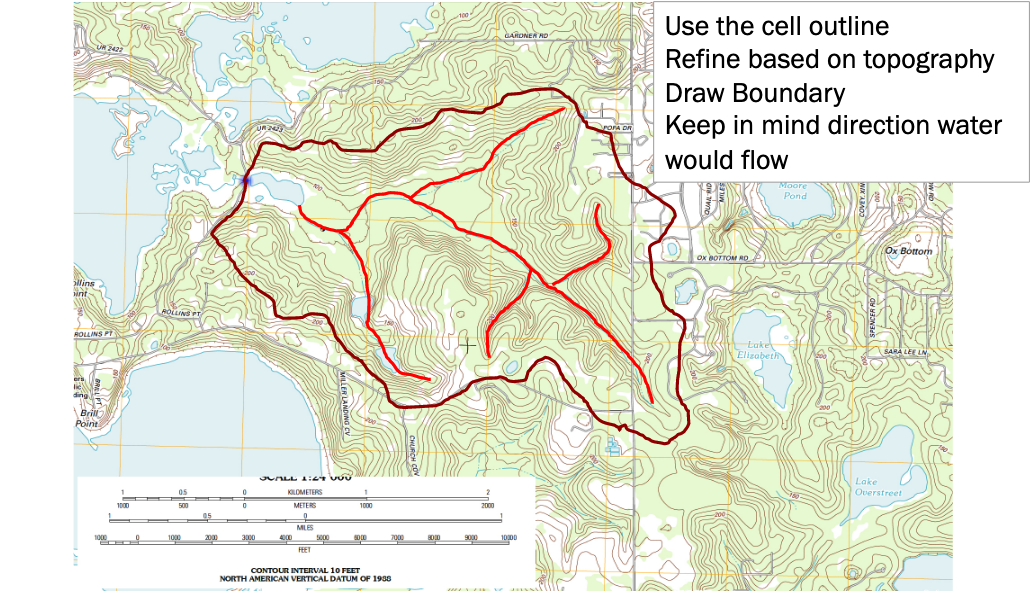
Use the grid to estimate average elevations in a grid cell, you use this information to help locate the boundary. Water flows from high to low elevation. Starting from the outlet work uphill until have high point, if its downhill as you cntinue in one direction beyond the point, its possibly the boundary (you are identifying “ridgeline” features).
Simultaneously identify internal water flow paths, these help identify the ridgeline features.
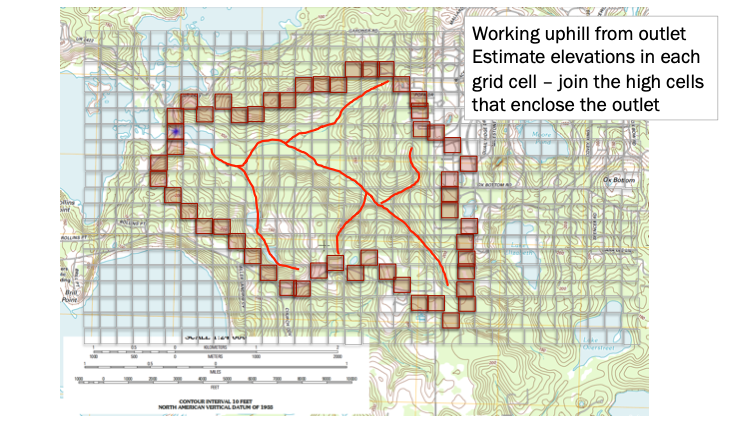
Step 3. Draw/Refine Boundary Estimates¶
Using the grid to estimate average elevations in a grid cell, you locate the coarse resolution boundary. Water flows from high to low elevation. Using the internal water flow paths, move upgradient along these paths to refine the boundary delineation.