FER - Water Quality, Testing, and Treatment (Environmental)#
Contributors
This webpage includes materials contributed by Dr. Evan Gray, subject-matter expert for this topic. Additional sources are cited where applicable; all other content was prepared by the JupyterBook’s author.
Readings#
Videos#
Example 1.#
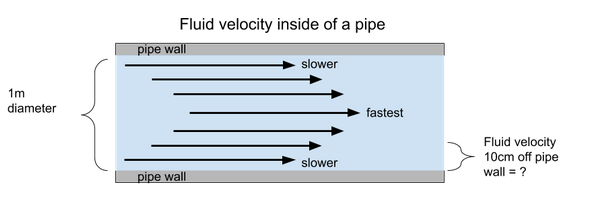
Flow in a circular pipe of diameter \(1~m\) has an average velocity of \(2.5~m/s\). What is the fluid velocity \(10~cm\) off the borders of the circular pipe? Assume laminar flow conditions.
A. 0.9 m/s
B. 1.8 m/s
C. 2.4 m/s
D. 0.2 m/s
Work it out#
Refer to Fluid Flow Characterization section in the Fluid Mechanics chapter of the FE Reference Handbook.
Flow in laminar flow conditions is assumed to have a triangular distribution where the fluid is moving the fastest at the center of the pipe and moving the slowest near the borders of the pipe. For laminar flow in a circular pipe, one can calculate what the fluid velocity is anywhere along the pipe radius via:
\(v(r)=v_{max}[1−(\frac{r}{R})^2]\)
where:
\(v_{max}=2 \bar v =2(2.5m/s)=5m/s\)
\(R\)=radius of the tube \(=1m/2=0.5m\)
\(r\)=distance from the centerline \(=0.5m−(10cm/100)=0.4m\)
\(v(0.4m)=5m/s[1−(\frac{0.4}{0.5})^2]=1.8m/s\)
Therefore, the fluid velocity 10 cm off the pipe border is \(1.8 m/s\), so choose B
Example 2#
One of the properties of polymers is:
A. they are generally organic compounds.
B. they are stable at high temperatures.
C. a combination of two or more materials differing in form or composition.
D. they are usually high density.
Work it out#
Refer to the Polymers section in the Materials Science/Structure of Matter chapter of the FE Reference Handbook.
Plastics (or polymers) are generally organic compounds based upon carbon and hydrogen. They are very large molecular structures. Usually they are low density and are not stable at high temperatures. They can be readily formed into complex shapes. Their strength, stiffness, and melting temperatures are generally much lower than those of metals and ceramics. Their light weight, low cost, and ease of forming make them the preferred material for many engineering applications.
Example 3#
Liquid nitrogen, when returned to the gaseous state, can displace oxygen from the air and can create an oxygen-deficient atmosphere under the right conditions.
The assertion above is:
A.True
B.False
Work it out#
Due to the large liquid to gas expansion that takes place upon evaporation, liquid nitrogen is capable of displacing sufficient oxygen to create an oxygen deficient environment in a small or insufficiently ventilated space, leading to the risk of asphyxiation.
Choose A
Note this question can concievably fall under the Ethics category as it pertains to compliance with regulations, codes, standards, and industrial safety.
Note
Nitrogen-enriched environments are sometimes used industrially as a fire suppression strategy. By lowering the partial pressure of oxygen, these environments prevent a fire from sustaining itself. They can still be entered by workers, but only for short periods of time.
Example 4#
The purpose of sludge dewatering is to:
A.Decrease total solids concentration
B.Increase total solids concentration
C.Convert suspended solids into settleable solids
D.None of these - sludge dewatering makes no change at all in solids concentration
Work it Out#
The primary goal of sludge dewatering is to increase the concentration of solids in the material that remains after treatment. When the solids content is higher, the amount of water that must be transported (per unit volume) is reduced.
This matters because disposal costs are usually based on the weight of the wet sludge (wet tons), not just the dry solids. If the sludge contains a lot of water, you end up paying to haul that water to the residuals handling or disposal site. By producing a drier “cake” with more solids, the volume and weight of water are minimized, which lowers the overall operating cost of hauling and disposal.
In short: effective dewatering means you pay to move solids, not unnecessary water.
Choose B