Exercise 2-1 (Problem 4.6 pp. 148)¶
The liquid pressure in the screen of a piezometer in a saline aquifer is $7.688 \times 10^{5} N/m^2$. The liquid density is 1055 kg/m$^3$ and the temperature is 14$^o$C. The elevation of the piezometer is 45.9 m above MSL.
Determine:
- The point-water pressure head.
- The fresh-water pressure head.
- The total fresh-water head.
Exercise 2-2 (Problem 4.8 pp. 148)¶
An aquifer has a hydraulic conductivity of 12 ft/day and an effective porosity of 0.17 and is under a hydraulic gradient of 0.0055. The water temperature is 14$^o$C and the mean pore diameter is 0.33 mm.
Determine:
- The specific discharge.
- The average linear velocity.
- If Darcy's law is applicable under these conditions; justify your answer.
Exercise 2-3 (Problem 4.10 pp. 148)¶
A confined aquifer is 18 m thick. The potentiometric surface drops 1.99 m between two wells that are 823 m apart. The hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer is 4.35 m/day
Determine:
- Discharge per unit width in the aquifer in cubic meters per day
Exercise 2-4 (Problem 4.13 pp. 149)¶
In the figure below (Fig. 4.19) the hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer is 14.5 m/day. The value of $h_1$ is 17.6 m, and the value of $h_2$ is 15.3 m. The distance from $h_1$ to $h_2$ is 525 m. There is an average recharge rate of 0.007 m/day.
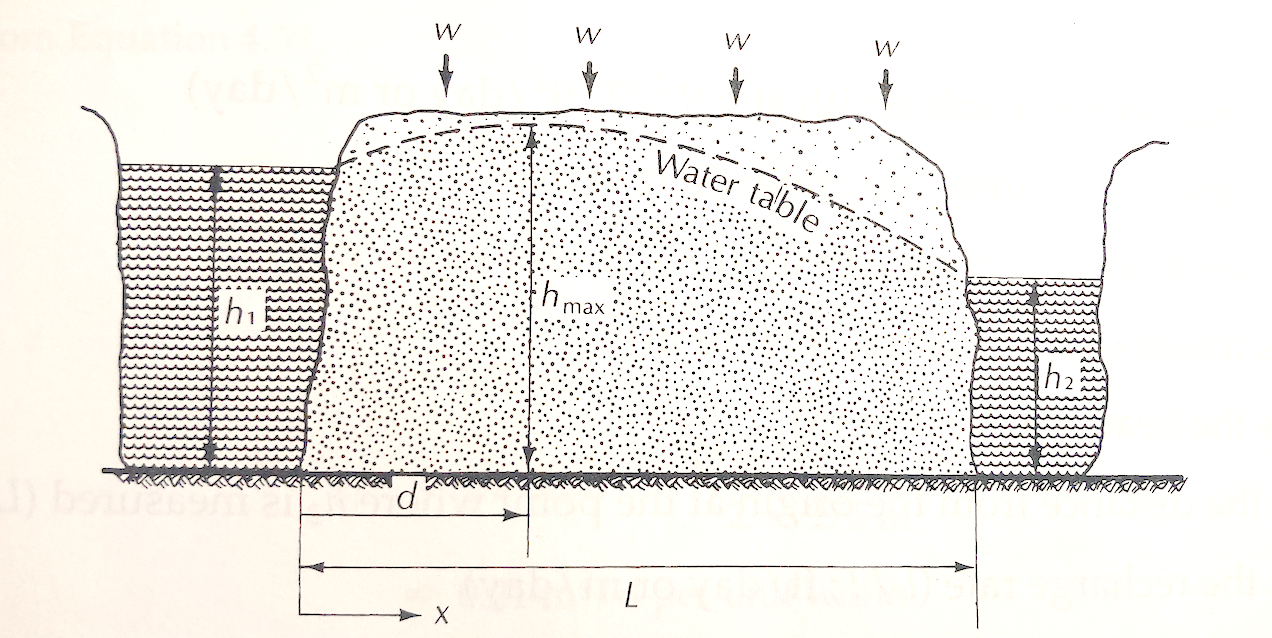
Determine:
- The average discharge per unit width at $x=0$.
- The average discharge per unit width at $x=525$.
- The location of the water-table divide (if it exists)
- The maximum height of the water table.
Exercise 2-5¶
Three monitoring wells exist in an aquifer as shown below. North is upward (toward the top of the page). The land surface elevations and depths to water are shown below.
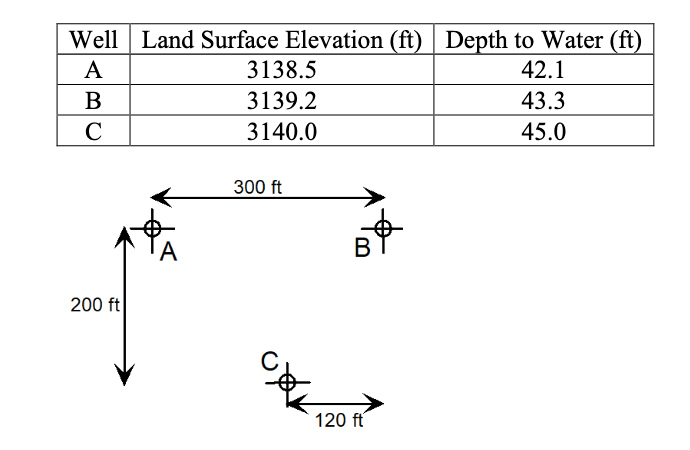
Determine:
- The magnitude and direction of the head gradient.
