CE 3305 Engineering Fluid Mechanics
Spring 2024 Exercise Set 8
LAST NAME, FIRST NAME
R00000000
Purpose :¶
Application of continunity to relate flow area and velocity to volumetric (or mass) flow rate. Application of definition of mean section velocity.
Assessment Criteria :¶
Completion, plausible solutions, use JupyterLab/Excel or a calculator. Application of problem solving protocol.
Problem 1.¶
A fluid flowing between two plates has a parabolic velocity profile given as $u(y)=\frac{4u_{max}}{h^2}(hy-y^2)$
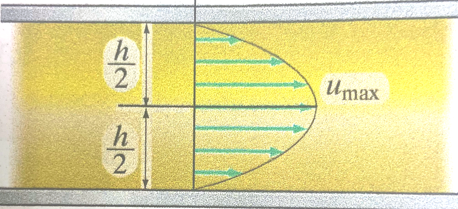
Determine:
- Average velocity in terms of $u_{max}$
- Volumetric discharge for plates of width $w$ (dimension into the sketch)
# sketch here
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution (step-by-step)
# discussion
Problem 2¶
Rain falls vertically onto the roof of a building with an average speed of 15 ft/s. The water accumulates in the gutter and flows out the downspout at 12 ft$^3$/min. The building is 18 feet wide.
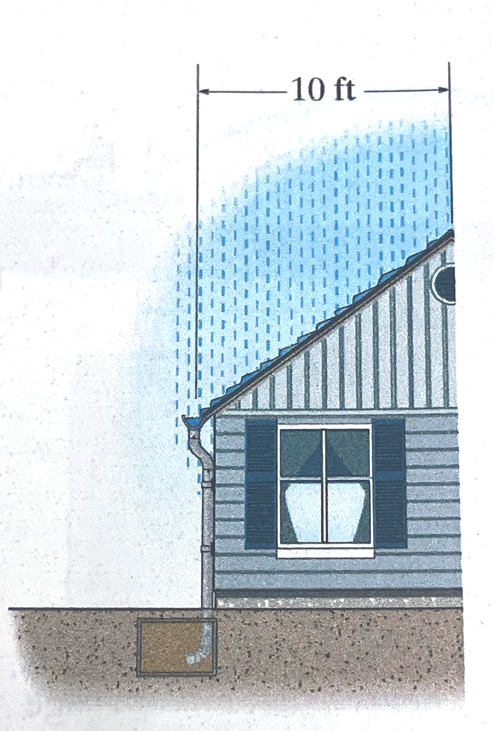

Determine:
- Amount of falling rainwater in one cubic foot of air.
- The number of drops in a cibic foot of air (drop diameter is 0.18 inches; $V_{drop}=\frac{4}{3}\pi r^3$)
# sketch here
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution (step-by-step)
# discussion
Problem 3¶
The velocity profile for a fluid in a circular pipe for fully developed turbulent flow is modeled using Prandtl's $\frac{1}{7}$ power law model: $u=U(\frac{y}{R})^{\frac{1}{7}}$
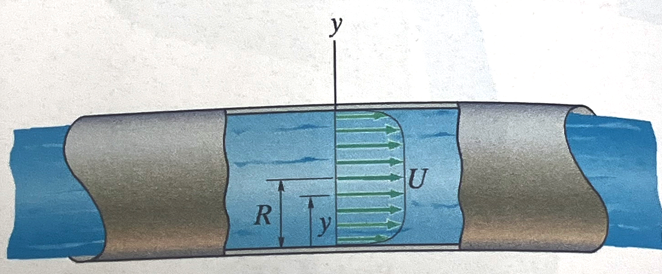
Determine:
- Average velocity (mean section velocity)
- Volumetric flow rate
# sketch here
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution (step-by-step)
# discussion
Problem 4¶
The pipe system is shown at steady flow with mean section velocities as indicated.
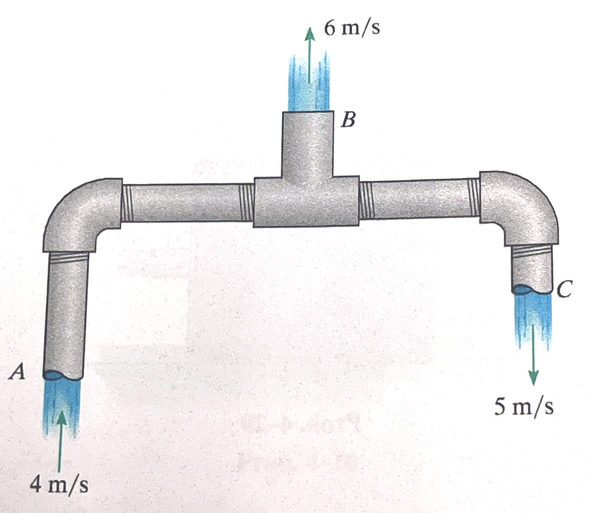
Determine:
- Outline (draw) a control volume that contains water in the pipe system.
- Indicate open control surfaces, and show outward pointing area vectors.
- Indicate flow velocities at these surfaces.
# sketch here
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution (step-by-step)
# discussion
