
Download this page as a jupyter notebook at Lab 9
LAST NAME, FIRST NAME
R00000000
ENGR 1330 Laboratory 9 - In-Lab
# Preamble script block to identify host, user, and kernel
import sys
! hostname
! whoami
print(sys.executable)
print(sys.version)
print(sys.version_info)
atomickitty sensei /opt/jupyterhub/bin/python3 3.8.10 (default, Jun 2 2021, 10:49:15) [GCC 9.4.0] sys.version_info(major=3, minor=8, micro=10, releaselevel='final', serial=0)

Numpy is the core library for scientific computing in Python. It provides a high-performance multidimensional array object, and tools for working with these arrays. The library’s name is short for “Numeric Python” or “Numerical Python”. If you are curious about NumPy, this cheat sheet is recommended: https://s3.amazonaws.com/assets.datacamp.com/blog_assets/Numpy_Python_Cheat_Sheet.pdf
A numpy array is a grid of values, all of the same type, and is indexed by a tuple of nonnegative integers. The number of dimensions is the rank of the array; the shape of an array is a tuple of integers giving the size of the array along each dimension. In other words, an array contains information about the raw data, how to locate an element and how to interpret an element.To make a numpy array, you can just use the np.array() function. All you need to do is pass a list to it. Don’t forget that, in order to work with the np.array() function, you need to make sure that the numpy library is present in your environment. If you want to read more about the differences between a Python list and NumPy array, this link is recommended: https://webcourses.ucf.edu/courses/1249560/pages/python-lists-vs-numpy-arrays-what-is-the-difference
import numpy as np #First, we need to impoty "numpy"
mylist = [2000,2001,2002,2003,2004,2005,2006,2007,2008,2009] #Create a list of the years
print(mylist) #Check how it looks
np.array(mylist) #Define it as a numpy array
[2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009]
array([2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009])
myotherlist = [[2000,2001],[2002,2003],[2004,2005],[2006,2007],[2008,2009]] #Since I want a 5x2 array, I should group the years two by two
print(myotherlist) #See how it looks as a list
np.array(myotherlist) #See how it looks as a numpy array
[[2000, 2001], [2002, 2003], [2004, 2005], [2006, 2007], [2008, 2009]]
array([[2000, 2001],
[2002, 2003],
[2004, 2005],
[2006, 2007],
[2008, 2009]])
Once you have created the arrays, you can do basic Numpy operations. Numpy offers a variety of operations applicable on arrays. From basic operations such as summation, subtraction, multiplication and division to more advanced and essential operations such as matrix multiplication and other elementwise operations. In the examples below, we will go over some of these:
import numpy as np #import numpy
Array1 = np.array([0,12,24,36,48,60,72,84,96]) #Step1: Define Array1
print(Array1)
print(Array1*2) #Step2: Multiple all elements by 2
print(Array1**2) #Step3: Take all elements to the power of 2
print(np.power(Array1,2)) #Another way to do the same thing, by using a function in numpy
print(np.max(Array1)) #Step4: Find the maximum value of the array
print(np.argmax(Array1)) ##Step4: Find the postition of the maximum value
print(np.min(Array1)) #Step5: Find the minimum value of the array
print(np.argmin(Array1)) ##Step5: Find the postition of the minimum value
Array2 = np.array([-12,0,12,24,36,48,60,72,84]) #Step6: Define Array2
print(Array2)
print(Array1+Array2) #Step7: Find the summation of these two arrays
print(Array1-Array2) #Step7: Find the subtraction of these two arrays
print(Array1*Array2) #Step8: Find the multiplication of these two arrays
[ 0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96] [ 0 24 48 72 96 120 144 168 192] [ 0 144 576 1296 2304 3600 5184 7056 9216] [ 0 144 576 1296 2304 3600 5184 7056 9216] 96 8 0 0 [-12 0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84] [-12 12 36 60 84 108 132 156 180] [12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12 12] [ 0 0 288 864 1728 2880 4320 6048 8064]
You can see it is considerably easier than manipulating as a list - be aware that the multiply above is element-by-element and not the inner product of two matrices (as was shown in Lesson 08)
import numpy as np #import numpy
Array1 = np.array([[5,10],[15,20]]) #Step1: Define Array1
print(Array1)
Array2 = np.array([[3,6],[9,12]]) #Step2: Define Array2
print(Array2)
print(Array1+Array2) #Step3: Find the summation
print(Array1-Array2) #Step3: Find the subtraction
MultArray = Array1@Array2 #Step4: To perform a typical matrix multiplication (or matrix product)
MultArray1 = Array1.dot(Array2) #Step4: Another way To perform a matrix multiplication
print(MultArray)
print(MultArray1)
print(np.min(MultArray)) #Step4: Find the minimum value of the multiplication
print(np.argmax(MultArray)) ##Step5: Find the postition of the maximum value
print(np.mean(MultArray)) ##Step6: Find the mean of the multiplication of these two arrays
print(np.mean(MultArray[0,:])) ##Step7: Find the mean of the first row of the multiplication of these two arrays
[[ 5 10] [15 20]] [[ 3 6] [ 9 12]] [[ 8 16] [24 32]] [[2 4] [6 8]] [[105 150] [225 330]] [[105 150] [225 330]] 105 3 202.5 127.5
Comparing two NumPy arrays determines whether they are equivalent by checking if every element at each corresponding index are the same.
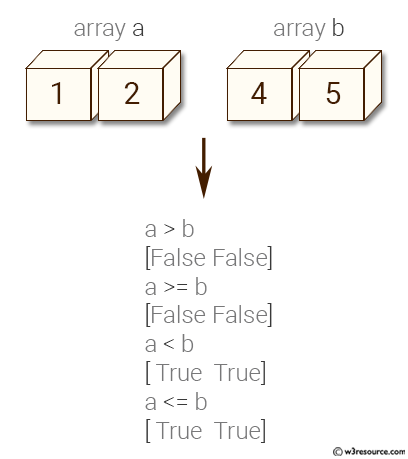
import numpy as np #import numpy
Array1 = np.array([1.0,2.5,3.4,7,7]) #Step1: Define Array1
print(Array1)
Array2 = np.array([5.0/5.0,5.0/2,6.8/2,21/3,14/2]) #Step2: Define Array1
print(Array2)
print(np.equal(Array1, Array2)) #Step3: Compare and see if the two arrays are equal
Array3 = np.array([6,1.4,2.2,7.5,7]) #Step4: Define Array3
print(Array3)
print(np.greater_equal(Array1, Array3)) #Step3: Compare and see if the two arrays are equal
[1. 2.5 3.4 7. 7. ] [1. 2.5 3.4 7. 7. ] [ True True True True True] [6. 1.4 2.2 7.5 7. ] [False True True False True]
numpy.copy() allows us to create a copy of an array. This is particularly useful when we need to manipulate an array while keeping an original copy in memory. The numpy.delete() function returns a new array with sub-arrays along an axis deleted. Here is a poctoral representation:
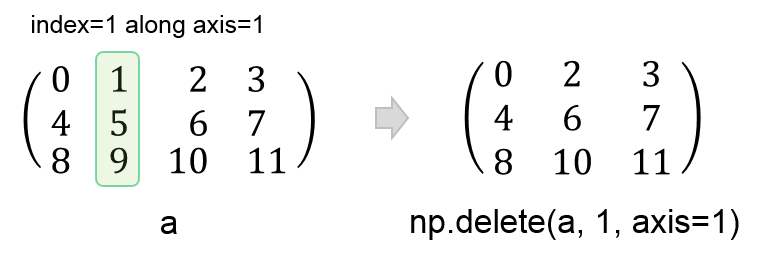
Here is another pictorial representation:
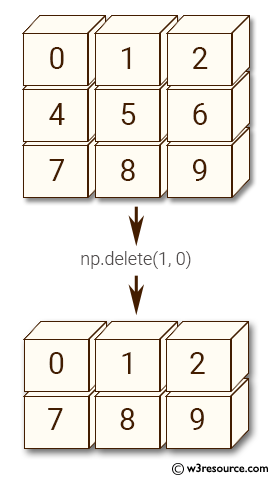
Let's have a look at the examples.
import numpy as np #import numpy
x = np.array([1,2,3]) #Step1: Define x
print(x)
y = x #Step2: Define y as y=x
print(y)
z = np.copy(x) #Step3: Define z as a copy of x
print(z)
# For Step4: They look similar but check this out:
x[1] = 8 # If we change x ...
print(x)
print(y)
print(z)
# By modifying x, y changes but z remains as a copy of the initial version of x.
x = np.delete(x, 1) #Step5: Delete the second element of x
print(x)
[1 2 3] [1 2 3] [1 2 3] [1 8 3] [1 8 3] [1 2 3] [1 3]
Sorting means putting elements in an ordered sequence. Ordered sequence is any sequence that has an order corresponding to elements, like numeric or alphabetical, ascending or descending. If you use the sort() method on a 2-D array, both arrays will be sorted.
Define a 1D array as ['FIFA 2020','Red Dead Redemption','Fallout','GTA','NBA 2018','Need For Speed'] and print it out. Then, sort the array alphabetically.
import numpy as np #import numpy
games = np.array(['FIFA 2020','Red Dead Redemption','Fallout','GTA','NBA 2018','Need For Speed'])
print(games)
print(np.sort(games))
['FIFA 2020' 'Red Dead Redemption' 'Fallout' 'GTA' 'NBA 2018' 'Need For Speed'] ['FIFA 2020' 'Fallout' 'GTA' 'NBA 2018' 'Need For Speed' 'Red Dead Redemption']
Define a 3x3 array with 17,-6,2,86,-12,0,0,23,12 and print it out. Then, sort the array.
import numpy as np #import numpy
a = np.array([[17,-6,2],[86,-12,0],[0,23,12]])
print(a)
print ("Along columns : \n", np.sort(a,axis = 0) ) #This will be sorting in each column
print ("Along rows : \n", np.sort(a,axis = 1) ) #This will be sorting in each row
print ("Sorting by default : \n", np.sort(a) ) #Same as above
print ("Along None Axis : \n", np.sort(a,axis = None) ) #This will be sorted like a 1D array
[[ 17 -6 2] [ 86 -12 0] [ 0 23 12]] Along columns : [[ 0 -12 0] [ 17 -6 2] [ 86 23 12]] Along rows : [[ -6 2 17] [-12 0 86] [ 0 12 23]] Sorting by default : [[ -6 2 17] [-12 0 86] [ 0 12 23]] Along None Axis : [-12 -6 0 0 2 12 17 23 86]
Slicing in python means taking elements from one given index to another given index.
We can do slicing like this: [start:end].
We can also define the step, like this: [start:end:step].
If we don't pass start its considered 0
If we don't pass end its considered length of array in that dimension
If we don't pass step its considered 1

Define a 1D array as [1,3,5,7,9], slice out the [3,5,7] and print it out.
import numpy as np #import numpy
a = np.array([1,3,5,7,9]) #Define the array
print(a)
aslice = a[1:4] #slice the [3,5,7]
print(aslice) #print it out
[1 3 5 7 9] [3 5 7]
Define a 5x5 array with "Superman, Batman, Jim Hammond, Captain America, Green Arrow, Aquaman, Wonder Woman, Martian Manhunter, Barry Allen, Hal Jordan, Hawkman, Ray Palmer, Spider Man, Thor, Hank Pym, Solar, Iron Man, Dr. Strange, Daredevil, Ted Kord, Captian Marvel, Black Panther, Wolverine, Booster Gold, Spawn " and print it out. Then:
import numpy as np #import numpy
Superheroes = np.array([['Superman', 'Batman', 'Jim Hammond', 'Captain America', 'Green Arrow'],
['Aquaman', 'Wonder Woman', 'Martian Manhunter', 'Barry Allen', 'Hal Jordan'],
['Hawkman', 'Ray Palmer', 'Spider Man', 'Thor', 'Hank Pym'],
['Solar', 'Iron Man', 'Dr. Strange', 'Daredevil', 'Ted Kord'],
['Captian Marvel', 'Black Panther', 'Wolverine', 'Booster Gold', 'Spawn']])
print(Superheroes) #Step1
print(Superheroes[:,0])
print(Superheroes[2,:])
print(Superheroes[4,2])
print(Superheroes[1:4,1:4])
[['Superman' 'Batman' 'Jim Hammond' 'Captain America' 'Green Arrow'] ['Aquaman' 'Wonder Woman' 'Martian Manhunter' 'Barry Allen' 'Hal Jordan'] ['Hawkman' 'Ray Palmer' 'Spider Man' 'Thor' 'Hank Pym'] ['Solar' 'Iron Man' 'Dr. Strange' 'Daredevil' 'Ted Kord'] ['Captian Marvel' 'Black Panther' 'Wolverine' 'Booster Gold' 'Spawn']] ['Superman' 'Aquaman' 'Hawkman' 'Solar' 'Captian Marvel'] ['Hawkman' 'Ray Palmer' 'Spider Man' 'Thor' 'Hank Pym'] Wolverine [['Wonder Woman' 'Martian Manhunter' 'Barry Allen'] ['Ray Palmer' 'Spider Man' 'Thor'] ['Iron Man' 'Dr. Strange' 'Daredevil']]

https://blog.finxter.com/collection-10-best-numpy-cheat-sheets-every-python-coder-must-own/
Put your answer in the empty markdown cell below; Make sure to cite any resources that you may use.
Use this markdown cell for your answer
Here are some of the resources used for creating this notebook:
Here are some great reads on this topic:
Here are some great videos on these topics: