Exercise 1-1 (Problem 3.7 pp. 110)¶
A constant-head permeameter has a cross-sectional area of 78.5 cm$^2$. A sample is 23 cm long. At an applied head differential of 3.4 cm, the permeameter discharges 50 cm$^3$ in 38 seconds.
Determine:
- The hydraulic conductivity in centimeters per second.
- The hydraulic conductivity in feet per day.
- The intrinsic permeability if the measurement is conducted at 15$^o$C.
- What type of soil is suggested by the hydraulic conductivity value.
Exercise 1-2 (Problem 3.10 pp. 111)¶
An aquifer has $S_y$ of 0.24. During a drought period, the following average water table declines were recorded:
| Area | Size(mi$^2$) | Decline(ft) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 12.5 | 1.33 |
| B | 19.8 | 0.88 |
| C | 23.8 | 3.98 |
| D | 9.56 | 2.34 |
| E | 12.3 | 4.44 |
| F | 7.22 | 0.34 |
Determine:
- The total volume of water represented by the decline in the water table.
Exercise 1-3 (Problem 3.13 pp. 111)¶
A confined aquifer has a specific storage of $4.033 \times 10^{-3} m^{-1}$ and a porosity of 0.274. The compressibility of water is $4.6 \times 10^{-10} m^2/N$.
Determine:
- The compressibility of the aquifer skeleton.
Exercise 1-4 (Problem 3.16 pp. 111)¶
An aquifer has three different formations. The uppermost formation A has a thickness of 8.4 m and a hydraulic conductivity of 22.3 m/day. The middle formation B has a thickness of 2.8 m and a hydraulic conductivity of 144 m/day. The lower formation C has a thickness of 33 m and a hydraulic conductivity of 35 m/day. Each formation is homogeneous and isotropic.
Determine:
- The overall horizontal hydraulic conductivity.
- The overall horizontal vertical conductivity.
Exercise 1-5 (Analysis B pp. 109)¶
The figure below (Fig. 3.32 pp. 110) is a map showing the ground-water elevations in wells screened in an unconfined aquifer in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. The aquifer is hydraulically connected to Lake Michigan, which has a surface elevation of 580 ft above MSL. Lakes and streams are also depicted on the map.
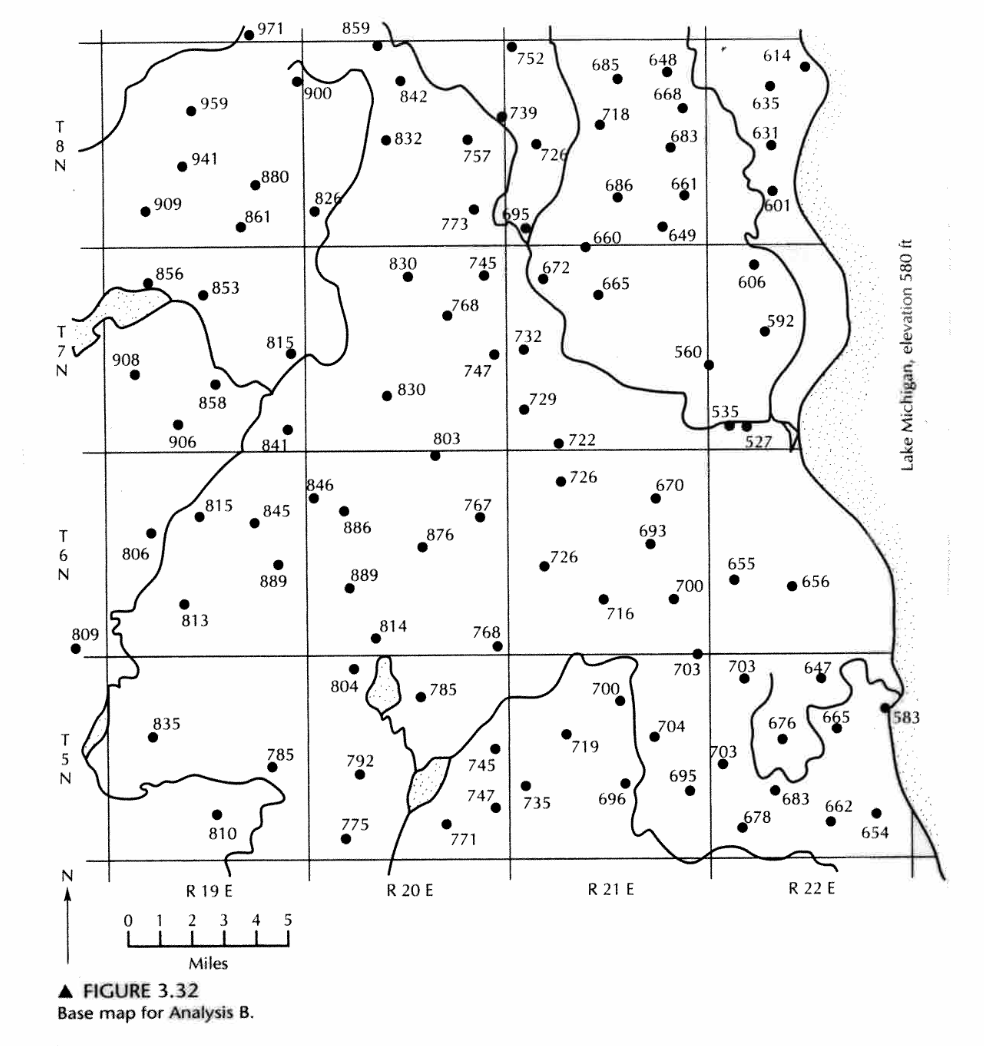
Determine:
- Make a water-table contour map with a contour interval of 50 ft starting at 550 ft.
- How groundwater levels are below the Lake Michigan surface elevation in part of the area.
