Download (right-click, save target as ...) this page as a Jupyterlab notebook from: ES-5
CE 4353 Design of Hydraulic Systems
CE 5360 Open Channel Flow
Fall 2023 Exercise Set 5
LAST NAME, FIRST NAME
R00000000
Purpose :¶
Apply principles of momentum conservation and rapidly varied flow concepts to open channel analysis and design
Assessment Criteria :¶
Completion, results plausible, format correct, calculations (Jupyter Notebook) are shown.
Instructions :¶
- CE 4353 Complete Problems 1-3
- CE 5360 Complete All Problems
Problem 1¶
A spillway chute and the hydraulic jump stilling basin at the end of the chute are rectangular in shape with a width of 80 ft. The incoming flow has a depth of 2.60 ft at a design discharge of 10,000 cfs. Within the basin are 20 baffle blocks that are each 3.0 ft high and 3.0 ft wide. Using an effective coefficient of drag of 0.6 for the baffle blocks, based on the upstream velocity and combined frontal area of the blocks
Determine:
- The sequent depth (ft) after the jump.
- The energy loss in ft in the basin with the blocks in place.
- The sequent depth (ft) after the jump without baffle blocks.
- The energy loss in ft in the basin without the blocks in place.
# sketch(s)
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution details (e.g. step-by-step computations)
# discussion
Problem 2¶
A river flows between bridge piers 3 m in diameter with a spacing of 15 m the downstream depth is 4.0 m and the downstream velocity is 2.5 m/s.
Determine:
- The approach depth using a coefficient of drag determined from the Figure below for the bridge piers.
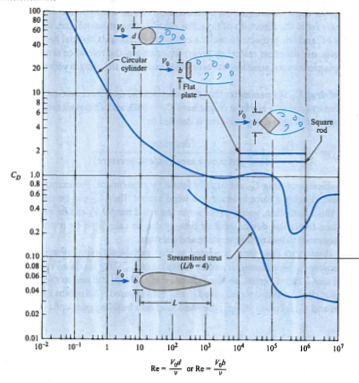
- The approach momentum function value $M_1$
- The exit momentum function value $M_2$
# sketch(s)
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution details (e.g. step-by-step computations)
# discussion
Problem 3¶
A straight-walled contraction connects two rectangular channels 12 ft and 7.2 ft wide. The discharge through the contraction is 300 cfs, and the depth of the approach flow is 0.815 ft.
Determine:
- The the downstream depth (ft)
- The Froude number
- The length (ft) of the contraction that will minimize standing waves
- If choking will occur
# sketch(s)
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution details (e.g. step-by-step computations)
# discussion
