Download (right-click, save target as ...) this page as a Jupyterlab notebook from: ES-4
CE 4353/5360 Design of Hydraulic Systems
Fall 2022 Exercise Set 4
LAST NAME, FIRST NAME
R00000000
Purpose :¶
Apply principles of momentum conservation and rapidly varied flow concepts to open channel analysis and design
Assessment Criteria :¶
Completion, results plausible, format correct, calculations (Jupyter Notebook) are shown.
Problem 1¶
A hydraulic jump occurs in a 20 ft wide rectangular channel, the upstream depth is 3.5 ft at a flow rate of 2500 cfs.
Determine:
- The downstream depth in ft
- The head loss across the jump.
# sketch(s) here
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution (step-by-step/computations)
# discussion
Problem 2¶
A hydraulic jump is to be formed in a trapezoidal channel with a base width of 20 ft and side slopes of 2:1. The upstream depth is 1.35 ft and Q=1100 cfs. Figure 3-2 below is from the textbook.
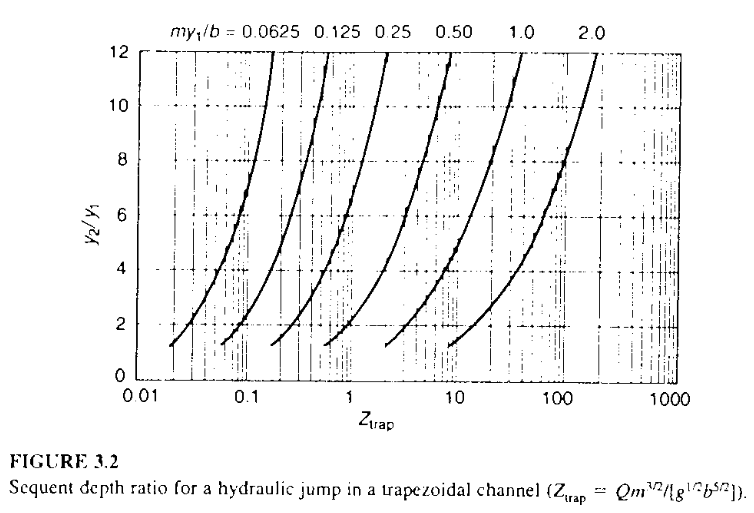
Determine:
- The downstream depth in the jump
- The head loss in the jump
- The approach momentum function value $M_1$
- The exit momentum function value $M_2$
# sketch(s) here
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution (step-by-step/computations)
# discussion
Problem 3¶
A 3-ft diameter storm sewer carries a discharge of 6.5 cfs with a flow depth of 0.65 ft. Figure 3-3 below is from the textbook.
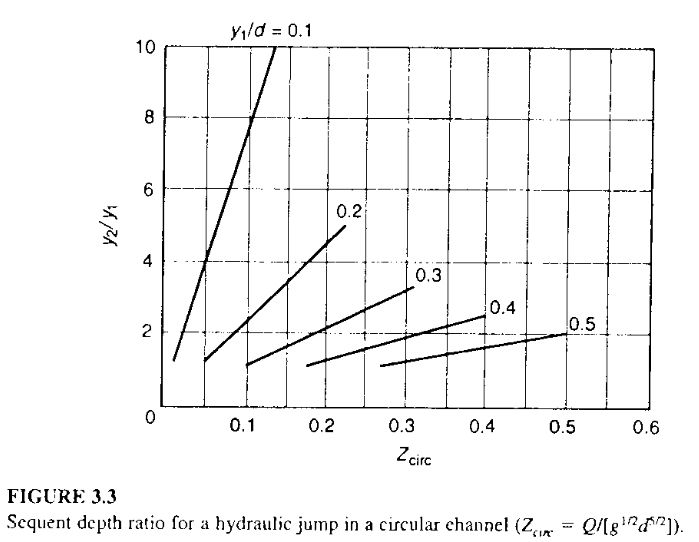
Determine:
- The downstream depth in the jump
- The head loss in the jump
- The approach momentum function value $M_1$
- The exit momentum function value $M_2$
# sketch(s) here
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution (step-by-step/computations)
# discussion
Problem 4¶
A flume with triangular cross section contains water flowing at a depth of 0.15 $m$ and at a discharge of 0.35 $\frac{m^3}{s}$. The side slopes of the flume are 2:1.
Determine:
- The downstream depth for a hydraulic jump
- The head loss in the jump
- The approach momentum function value $M_1$
- The exit momentum function value $M_2$
# sketch(s) here
# list known quantities
# list unknown quantities
# governing principles
# solution (step-by-step/computations)
# discussion