Download this file as a Jupyter Notebook@ http://54.243.252.9/ce-3372-webroot/2-Exercises/ES6/ES6.ipynb
ES-6¶
Copyright © 2021 Theodore G. Cleveland
Purpose:¶
Demonstrate flow-equalization volume required for a storage tank to leverage some constant flow rate.
- Analyze daily water cumulative demand (from time varying outflows)
- Find equivalent constant draw rate
- Use double mass curve concept to find maximum deviations to size an equalization tank.
Problem Data¶
Figure 1 is a plot of variable cumulative inflow volume versus time for a proposed flow-equalization tank location and the equivalent constant rate inflow for the same location.
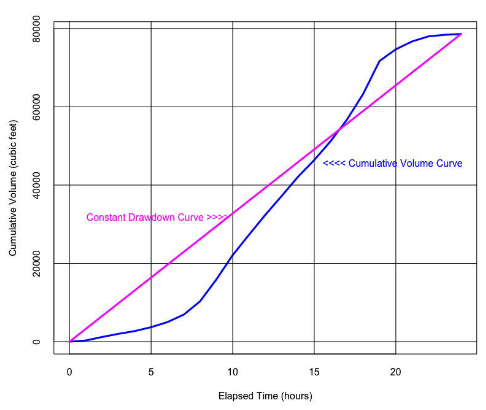
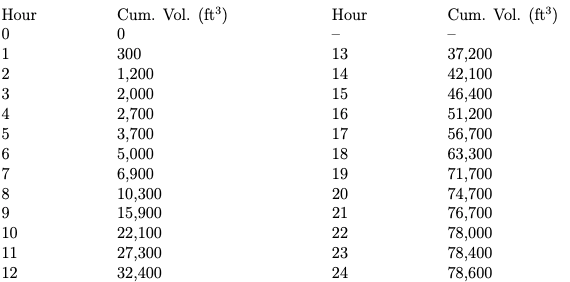
Table 1 is a list of time and cumulative volume inflow (same as the graph). A flow-equalization storage tank volume is to be determined.
Using the supplied problem data (either graph or table or both):
- Determine the cumulative volume of inflow (or draft) every 24 hours plotted on Figure 1 and tabulated in Table 1.
- Determine the constant flow rate (cubic feet per hour) from the constant drawdown curve plotted on Figure 1 and tabulated in Table 1.
- Determine the largest maximum absolute deviation between the constant drawdown line and the variable inflow curve indicated by Figure 1 and/or Table 1
- Determine the second largest maximum absolute deviation between the constant drawdown line and the variable inflow curve indicated by Figure 4 and/or Table 1
- Determine a recommended flow equalization storage volume indicated by Figure 4 and/or Table 1
Deliverables:¶
A brief report with your solution, showing the requested values, intermediate calculations, and the recomended equalization storage requirement.
References¶
- Gupta, R. S. 2017. Hydrology and Hydraulic Systems. Waveland Press, Inc. pp. 548-552